Knowing the anatomy of a ferret will help you take the best care of your pet. Ferrets are curious, active, and social animals, which makes them one of the most lovable household pets across the globe.
It has been two years since I started understanding ferret anatomy. My veterinarian helped a lot to understand the ferret’s body inside out.
I applied all the learning and now I’m an expert in handling and understanding the internals of pet ferrets. Being a ferret owner for more than five years, it was practically easy to know the basic anatomy of the ferret.
You don’t need to worry, in this article, I’m explaining the ferret inside out, which will create the best bond between you and your furry friend.
Content List
- 1 Anatomy of a Ferret
- 2 Ferret teeth
- 3 Ferret skeleton
- 4 Ferret reproductive system
- 5 Ferret digestive system
- 6 Ferret senses
- 7 Ferret body size and weight
- 8 Do ferrets have bones?
- 9 Do ferrets have spines?
- 10 Do ferrets have anal glands?
- 11 Why do ferrets have sharp teeth?
- 12 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 13 Conclusion
Anatomy of a Ferret
To understand the anatomy of a ferret, first, you need to understand the nature and behavior of a ferret.
Ferrets belong to the Mustelidae family and are quite related to other animals like mink, otters, weasels, and stoats. They are quite friendly and love being around humans and other animals.
Ferrets are carnivores in nature which means they hunt for prey. Rabbits, rats, mice, and more are the prey of ferrets. A ferret has sharp teeth which enable it to grab prey from the neck and body.
The bodies of ferrets are also very flexible which them the freedom to quickly move and jump while chasing prey. Their body is long and slim which is a major benefit in catching prey from small places or holes.
Basic ferret anatomy
Basic ferret anatomy is the study of the ferret body from the inside out.
Basic ferret anatomy involves the study of the ferret reproductive system, ferret skeleton, ferret digestive system, ferret spine, ferret senses, size, and weight.
You will get to know about the basic anatomy of a ferret.
Ferret teeth
Ferret teeth are the most basic and primary thing that make them a carnivore animal. Teeth growth in ferrets started after 4 weeks of the birth.

This is the first stage of teeth growth in which the eruption of deciduous teeth takes place. Soon the second stage of teeth growth occurs in which permanent ferret teeth develop.
After the permanent growth of your ferret teeth, you must contact a veterinarian once a year for a dental checkup. You never know when your furry friend start having oral pain and dental issues.
Ferret milk teeth
As mentioned above a milk or deciduous teeth started growing after 4 weeks of ferret birth. There are usually 28 to 30 teeth in this phase of ferret. From 6 weeks of ferret birth onwards they start having permanent teeth.
Permanent ferret teeth
The permanent ferret teeth start growing after 6 to 8 weeks of birth of ferrets. There are 34 permanent ferret teeth which give extra benefit in hunting.
After achieving this stage the ferrets are abandoned by their mother and start eating proper ferret foods. Due to a short crown with a limited pulp canal, ferrets have extra strong teeth.
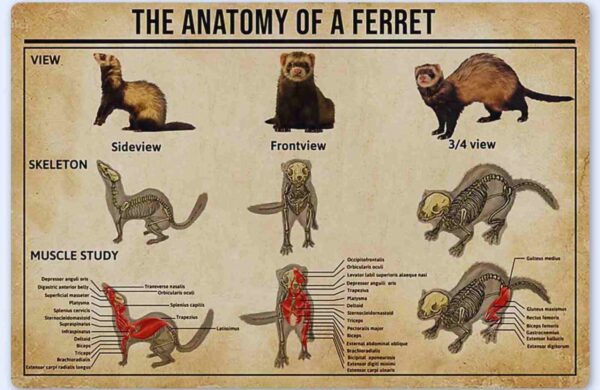
Ferret skeleton
The skeleton of a ferret is the same as other carnivore mammals. A fully grown ferret has 200 bones which is a close resemblance to the human being.
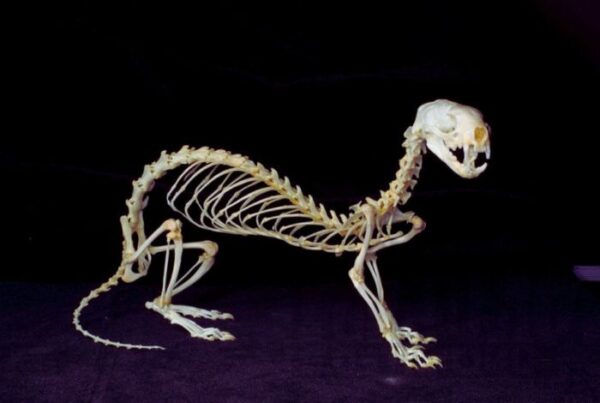

However, there is still a difference in the bone arrangement in the ferrets which makes them unique from the others. There are primarily three sections that define the anatomy of the ferret skeleton.
Axial skeleton
The axial skeleton is the core part of the ferret skeleton. It sets the base of the skeleton structure of ferrets. This is made up of the skull, ribs, vertebrae, and sternum.
Appendicular skeleton
The appendicular skeleton is the second most important part which defines the anatomy of the ferret skeleton. As a ferret owner, you must have a basic understanding of the appendicular ferret skeleton.
It consists of the pelvis, shoulder, bones of the front limbs, and rear limbs.
Heterotopic skeleton
The heterotopic ferret skeleton is the construct of fabella and kneecaps in a tissue of the real limbs.
Ferret reproductive system
If there are any top things you need to know about your ferret it would be the reproductive system of your pet.
Most good and bad things begin and end with the reproductive system of the ferret.
If you understand it then you are majorly qualified to know the anatomy of a ferret.
Typically the sexual maturity in ferrets takes place from 8 to 12 months. The female ferret lived under the heat phase after gaining sexual maturity and they continue to live from matting to bred and finally giving birth.
While a male ferret exhibits an intense odoriferous odor during the breeding season. Male ferret secures their space by urinating.
Both female and male ferrets become extremely fertile during the breeding phase.
Ferret digestive system
The digestive system of ferrets is quite easy to understand and it’s relatively the same as other mammals.
Ferret digestive system consist of duodenum, jejuno-ileum, colon and rectum. The stomach of a ferret doesn’t have a caecum and ileocolic valve.
As the length of the ferret’s body is larger results in a large stomach. For better digestion, ferrets secrete hydrochloric acid which helps in digesting eaten meals.
The ferret small intestine is about 182-198 cm long, while the large intestine is only 10 cm long. The ferret colon length is 7cm.
Due to the smaller digestive tract food doesn’t last a long period in the ferret’s stomach.
In an adult ferret, it took 3-4 hours to fully digest the food, while it took only about 1 hour for ferret kits to digest. However, for smooth ferret digestion, avoid giving carbohydrates to your pet ferret
Ferret senses
Ferrets have a very strong sense of smell. The sense capability of ferrets even crosses human beings and dogs.
Your furry friend uses their excellent senses during hunting. Most of the time ferrets predict prey position, distance, and speed through their sense of power.
Ferrets compensate for poor or less strong eyesight from the power of sense.
Ferret body size and weight
Ferrets consist of a typical mustelid body shape, being long and slender. A ferret’s body length lies between 46 and 61cm and it is the same as mink. The ferret tail is about 13-15cm long.

The weight of the ferret is between 0.7-2.0kg. However, a male ferret is slightly heavier than a female ferret. An adult male ferret weight is 2-4 pounds and a female ferret weight is around 1 pound 6 ounces.
Such balance length and weight are major contributors to the great flexibility of the ferret.
It’s important to note these parameters aren’t absolute. The change is minimum and maximum limit is possible.
Do ferrets have bones?
Yes, ferrets have bones. Ferrets roughly have around 200 bones which contributed to the formation of the ferret skeletal system.
There are various kinds of bones in the ferret’s body that participate in skeletal formation. The ferret bone type, structure, and dimension play a vital role in such an excellent, flexible ferret body.
Ferret bone structure
Various structures of bones play various in the ferret body. Mentioning some of them:
- The axial skeleton is made up of the skull, vertebrae, ribs, and sternum.
- The bones of the front arms, rear legs, shoulders, and pelvis form the appendicular skeleton.
- The bones of the front arms are light and short.
- The front paws have five clawed digits.
- The vertebral column is long and very flexible, which allows a ferret to go into a narrow tunnel, and do a U-turn which helps a lot during hunting prey.
Do ferrets have spines?
Yes, ferrets have spines because it’s a mammal and all mammal animals have spines.
The spines of ferrets are extremely flexible which helps in quickly run, move, and stop without any injury. Due to the presence of 15 thoracic, vertebrae, 5 lumbar, and 3 sacral vertebrae, ferrets can bend their body in the desired way.
The extent of bend that a ferret’s body shows is impossible to us as human beings and also not possible for many animals out there.
Do ferrets have anal glands?
Yes, ferrets have anal glands which typically measure 10mm × 5 mm.
The anal glands in ferrets are fully developed and present in pair, which generates a serous yellow liquid with a strong odor.
Usually, an annoyed and frightened releases yellow watery fluid. But, ferrets can throw the liquid over long distances.
Why do ferrets have sharp teeth?
Like us ferrets also have four types of teeth namely, the incisors, canines, premolars, and molars only different in the number of each type of tooth.
Ferrets are carnivore animals which means they eat meat as their prime food and are predators of many animals.
To catch food or prey, ferrets need a good grip which is fulfilled by their sharp teeth. Like humans and rabbits, the teeth of ferrets also stop growing.
Mentioning the position and working of ferret teeth:
- The front ferret teeth are incisors. They are used in picking the food.
- The canine teeth are sharp which are used to tear the food.
- The premolar ferret teeth are used for cutting and shearing the food.
- Molars ferret teeth are used to grind the food for digestion.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Do ferrets have sharp teeth?
Yes, adult ferrets have sharp teeth which they use to tear and bite prey.
Why do ferrets choke?
Ferrets choke or sneeze in the reverse direction to clear undesired material from their throats.
Do ferrets have strong jaws?
Yes, ferrets have strong jaws especially black-footed ferrets have tan bodies with more strong jaws.
Conclusion
Now, I can say you have a full understanding of the anatomy of a ferret.
Ferret anatomy involves the study of the reproductive system, ferret skeleton, ferret digestive system, spine of ferret, ferret senses, size, and weight.
Having an understanding and knowledge of these ferret organs will make you take the best care of your furry friend.